Have you ever had that “aha” moment with numbers on a balance sheet? The world of finance can seem distant and hard to understand. But there’s a simple truth within the complexity: knowing your manufacturing costs matters a lot for your business’s health. It’s a common pressure—making sure the budget is right and production meets targets. This is where production volume variance comes in. This key figure lets you see if your actual production matches your budgeted goals. It highlights how well you manage costs and efficiency. By mastering variance analysis, you’re not just dealing with numbers. You’re making smarter choices for your business’s profit.
Key Takeaways
- Production volume variance measures the difference between actual and budgeted production costs.
- The formula for calculating production volume variance considers actual and budgeted units alongside overhead rates.
- Favorable variances may indicate cost efficiency, while unfavorable variances require closer examination.
- Understanding fixed and variable costs is essential for comprehensive variance analysis.
- Production volume variance impacts strategic decisions in managing manufacturing costs.
Understanding Production Volume Variance
Production volume variance is a key idea in making things. It shows the gap between how much was actually made and the planned amount. Keeping track of this difference helps businesses know how well they’re doing. It also guides them in handling their costs better.
Definition and Importance
The definition of production volume variance involves comparing what was really made to what was expected. This comparison is essential for many reasons: First, it allows business owners and managers to assess the efficiency of their production processes. If the actual production volume is less than expected, it could indicate that there are inefficiencies or bottlenecks in the production line that need to be addressed. On the other hand, if the actual production volume exceeds expectations, it could indicate that the production process is running smoothly and efficiently. Understanding production variance also allows businesses to identify any unexpected costs or savings associated with production. By analyzing the reasons behind the variance, businesses can make informed decisions about how to improve their production processes and maximize their profits.
- It gives production variance insights by showing how production meets financial plans.
- Watching this variance helps check manufacturing efficiency and how well resources are used.
- Knowing how overhead costs change with production levels improves planning and budgeting.
When more items are made, fixed overhead costs, like rent and buying equipment, spread over more products. This usually means more profit. But, costs that change, like materials and storing stuff, depend on how much is produced. So, it’s crucial to keep a good balance.
Key Takeaways
Here are important points about production volume variance:
- Making more goods lowers the cost for each one, which means better profit and efficiency.
- Differences between actual and planned production might improve or worsen cost situations.
- Handling production variance well goes hand in hand with steady production. This helps in making accurate budgets and financial predictions.
In the end, really understanding production volume variance lets businesses make smarter choices about how they produce things and plan their finances.
What is the Production Volume Variance?
The production volume variance is key for checking how well manufacturing works. It shows the difference between what actually cost and what was thought would cost. This affects how much money you make.
Formula for Calculation
The formula to find the production volume variance is:
Production Volume Variance = (Actual Units Produced – Budgeted Production Units) x Budgeted Overhead Rate per Unit.
This production volume variance formula helps figure out how your making levels affect your budget. Knowing if you made more or less than planned can really help with your budget.
Examples of Application
Seeing how the production volume variance works in real life can improve how you do things. For example, a company expected to make 8,000 units but made 9,400 instead. They ended up making $28,000 more because of this.
- Actual Units: 9,400
- Budgeted Units: 8,000
- Budgeted Overhead Rate: Assume $3.00 per unit
But, if another company thought they’d make 10,000 units and only made 7,400, they lost money instead.
- Actual Units: 7,400
- Budgeted Units: 10,000
- Budgeted Overhead Rate: Assume $5.00 per unit
These application examples show how important it is to keep an eye on your production volume variance. Understanding and managing your costs well can make your operation more efficient and profitable.
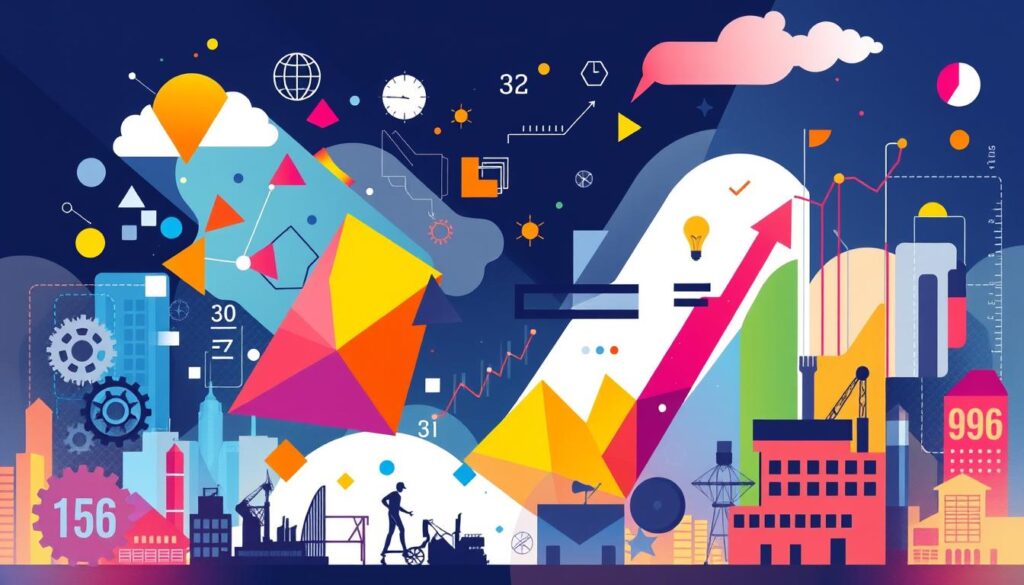

| Scenario | Actual Units Produced | Budgeted Units | Overhead Rate per Unit | Variance Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Favorable Outcome | 9,400 | 8,000 | $3.00 | $28,200 |
| Unfavorable Outcome | 7,400 | 10,000 | $5.00 | -$13,000 |
Factors Influencing Production Volume Variance
It’s key for companies to grasp what affects production volume variance. This helps them fine-tune costs and boost financial results. Both fixed and variable costs are important, affecting financial outcomes greatly.
Fixed and Variable Costs
Fixed costs don’t change with production levels. Think of costs like rent, insurance, and salaries. Managing these costs well means spreading them over more units when production goes up. This reduces the cost for each unit, boosting profits.
Variable costs, however, change with how much you produce. Costs for materials and shipping go up or down with production changes. Knowing how fixed and variable costs interplay helps businesses plan their budgets and manage money better. For example:
- Labor costs greatly affect total production costs.
- Costs for raw materials can change a lot, depending on supply and demand.
- Energy costs are also crucial in figuring out production costs.
Impact of Production Volume on Financial Performance
How much you produce directly affects your finances. If you produce more than planned, costs spread out over more units. This makes each unit cheaper and boosts profit margins. But, producing less increases the cost per unit and pressures finances.
To handle these issues, keep an eye on the market and expect changes. Key points to consider include:
- 93% of sales pros find predicting sales tough, even near the sales cycle’s end.
- Sales rep performance and pricing strategies greatly influence your production.
- Seasonal trends and what competitors charge also affect your decisions.
Understanding the link between fixed costs, variable costs, and production volume helps align business practices with financial objectives.

Good vs. Bad Production Volume Variance
It’s key to know the difference between good and bad production volume variances for managing finances well. A good variance means making more than planned, which makes each item cheaper because of spreading fixed costs. A bad variance is when you make less, making each item cost more, and this hurts profits.
Favorable and Unfavorable Outcomes
Understanding both good and bad outcomes helps businesses spot what needs to get better. A good variance points to effective operations and can boost profits. A bad variance shows where problems might be, needing attention. This way, businesses face:
- Favorable Variance: Making more than expected helps spread out fixed costs, lowering inventory expenses.
- Unfavorable Variance: Producing less than expected raises unit costs and can cause money worries.
Implications of Low Production
Not making enough can have big downsides for a business. It can lead to:
- Higher costs for each item, which can eat into profits.
- The risk of having too much stock, which might not sell and costs more to keep.
- Issues with cash flow, as making less can slow down money coming in.
Matching production to what the market wants is vital to avoid these issues. It helps use resources well and keeps costs down, building a stronger financial ground for the company.

Conclusion
Understanding production volume variance is key for businesses wanting to control costs and increase profits. This variance shows how well a company meets its production targets compared to its budget. It helps guide changes in operations, matching real results with what was expected.
Knowing why production volume variances happen is also important. They can come from inside the company, like planning, or from outside, like market demand. Seeing these reasons helps make smart choices. By checking your production volume variance often, you can make changes to make your operations better.
Managing production volume variance well can improve your company’s finances and help you use resources smartly. This keeps your business going strong. Regularly analyzing these variances points out where you can get better, leading to more efficient and stable operations.